Table of content
Introduction
The days when trading was only for men in suits shouting across the floor of Wall Street are gone. Today, all it takes is a smartphone or a computer and an internet connection. With just a few taps, anyone, from students to stay-at-home parents can buy and sell stocks, cryptocurrencies, or foreign currencies from the comfort of their home.
Apps like Robinhood, Coinbase, and eToro have revolutionized the financial world. Now, trading is accessible to everyone, not just big banks or financial institutions. Whether you’re buying Bitcoin between classes or selling shares of your favorite company from your living room, trading has never been easier than it is now.
So What Is Trading?
Trading simply means buying and selling assets to make a profit. You aim to buy something at a lower price and sell it at a higher one. The difference between the buying and selling price is the profit.
These assets can include:
- Stocks (like Apple or Tesla)
- Cryptocurrencies (like Bitcoin or Ethereum)
- Forex (foreign currencies) (like USD, EUR, JPY)
- Futures (like gold, oil, or wheat)
Example: An individual buys Bitcoin for $90,000. A week later, it’s worth $96,000. They sold it and just made $6,000 in profit.
Who Can Trade?
One of the biggest myths is that trading is only for experts with finance degrees. In reality, almost anyone can start trading today, as long as they meet a few simple conditions.
Finding a Reliable Broker
Choosing the right broker is one of the most important steps. A broker acts as your gateway to the markets so reliability matters. Look for one that is regulated by a respected financial authority (like the FCA in the UK, CySEC in Cyprus, or ASIC in Australia). Avoid unregulated brokers promising “guaranteed profits” or unrealistic bonuses.
Anyone with Internet + Capital
The basic requirements are simple: a device (phone, tablet, or computer), an internet connection, and some starting money. You don’t need thousands of dollars to get started. Many brokers allow accounts with as little as $50–$100, and some even let you begin with demo accounts where you risk nothing but practice.
Trading vs. Investing: What’s the Difference?
Trading and investing often get confused, but they are not the same thing. Both involve putting money into markets, but the goals, timeframes, and risks are very different.
Aspect | Trading | Investing |
Goal | Profit from short-term price changes (buy low, sell high quickly). | Build long-term wealth through growth, dividends, or steady appreciation. |
Timeframe | Minutes, hours, days, or weeks. | Years or even decades. |
Approach | Frequent buying and selling, reacting to market movements. | Buy and hold fewer transactions, less focus on daily market swings. |
Risk Level | Higher risk due to short-term volatility and frequent exposure to losses. | Generally lower risk, but still exposed to market downturns. |
Skills Needed | Strong focus on timing, technical analysis, and emotional control. | Patience, long-term perspective, and belief in fundamentals. |
Can You Do Both?
Trading and investing don’t have to be opposites, everyone can combine them. Many people build a long-term investment portfolio for stability while also trading on the side for short-term opportunities.
This way, investments provide a solid foundation, while trading adds flexibility and the chance to profit from short-term market moves.
The Main Markets You Can Trade
When people talk about “the markets,” they’re not just talking about one thing. There are many different types of markets, each with its own opportunities and risks. Here are the main ones beginners usually come across:
Forex (Currencies Pairs)
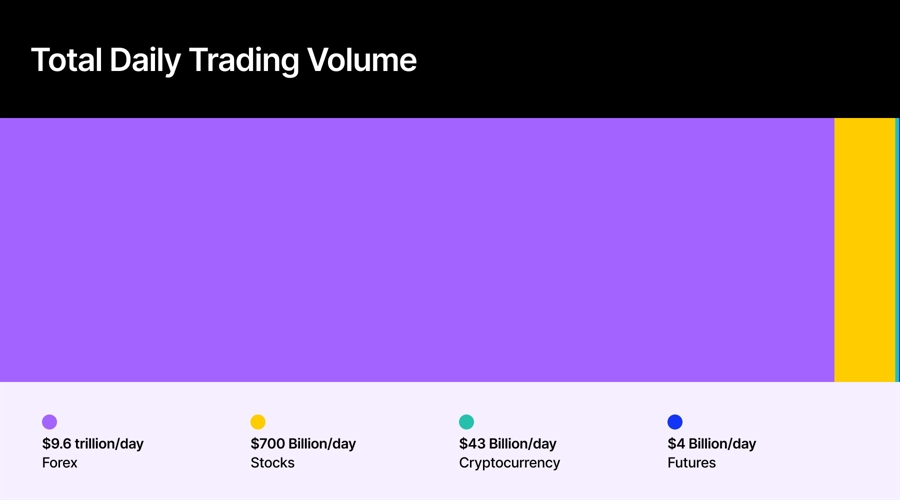
The foreign exchange market, better known as Forex or FX is where traders buy and sell global currencies. It’s the largest and most liquid market in the world. In fact, the Triennial Central Bank Survey reported more than $7.5 trillion in daily trades.
Real-life example: Imagine someone bought EUR/USD at 1.1650, expecting the euro to rise. If the price climbs to 1.1700, they make a profit because their euros are now worth more in U.S. dollars. But if it falls to 1.1600 instead, they take a loss, since their euros are now worth less.
If you want to learn more about Forex trading, you can find our What is Forex Trading Beginner Guide to help you out with your journey.
Stocks (Companies)
Stock trading means buying and selling shares of companies. If an individual buys Tesla stock and its price rises, they can sell it for a profit.
Real-life example: Suppose an individual buys Tesla shares at $329 each. If the price later rises to $350, selling earns them a healthy profit. But if the stock drops to $280 instead, they would be selling at a loss.
If you want to learn more about Stock Trading you can find our What is Stocks Trading Beginner guide to help you out with the journey.
Cryptocurrencies (Digital Assets)
Crypto is a relatively new market, famous for its high volatility. Coins like Bitcoin or Ethereum can rise or fall by double-digit percentages in a single day.
Real-life example: Someone who bought Bitcoin at $100,000 and sold when it hit $120,000 made a 20% profit. But if the price dropped back to $80,000 instead, they’d face a big loss just as quickly.
If you want to start Crypto Trading check out our beginner guide on What is Cryptocurrency Trading to help you understand more about this asset and with your journey.
Futures (Gold, Oil, Silver, etc.)
Futures are physical goods traded in global markets. Common ones include gold, oil, wheat, and coffee. They’re often influenced by supply and demand, weather, or global events.
Real-life example: A trader who bought gold at $3,000 could sell at $3,500 for a $500 profit. But if gold slipped to $2,850, they’d be looking at a loss instead.
Indices (S&P 500, NASDAQ, etc.)
An index tracks the performance of a group of stocks. For example, the S&P 500 measures 500 large U.S. companies. Instead of trading on one company, traders can speculate on the overall market.
Real-life example: If you buy the SP500 index at 15,000 points and it rises to 15,500, you profit from the move. But if it drops to 14,500, that same position would mean a loss.
CFDs (Contracts for Difference)
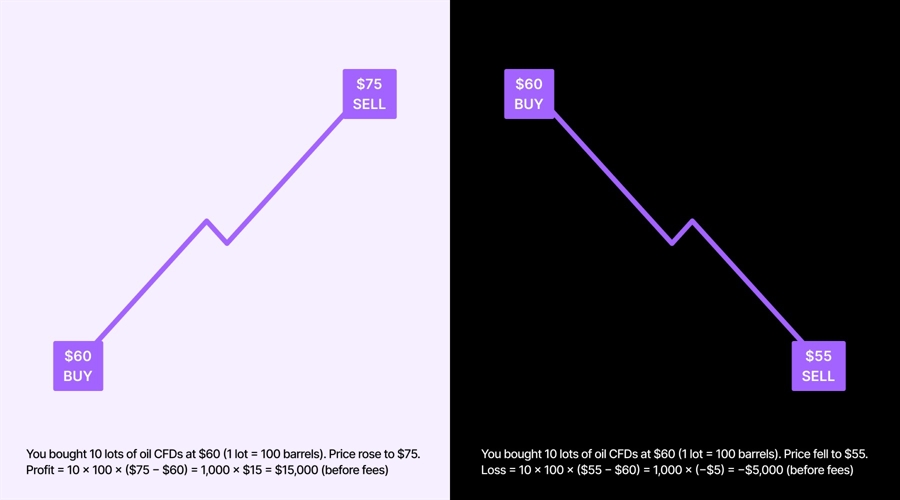
CFDs let traders speculate on price movements without actually owning the asset. You don’t need to buy the actual stock, oil barrel, or Bitcoin, you just trade on the price difference.
Real-life example: Let’s say someone opened a CFD trade on oil when it’s $60. If the price climbs to $75, they profit from the $15 increase. But if it falls to $55, they would take a loss instead.
If this type of trading caught your interest and you want to learn more about it, you have to read our guide on What is CFD Trading before starting to help you out understand more about CFDs and help you out with your trading journey.
Light Regulations You Should Know
You don’t need a license to be a trader, but there are legal boxes to tick. Most brokers will require:
- That you are at least 18 years old.
- Proof of identity (passport or ID card).
- Proof of address (like a utility bill).
This process is called KYC (Know Your Customer), and it’s standard in financial services. It ensures the broker complies with regulations and keeps your account safe.
No Degree Needed
Unlike traditional finance careers, trading doesn’t require a diploma or professional certification. What matters most is your ability to learn, practice, and manage risk. Resources are everywhere: books, free YouTube tutorials, webinars, and demo accounts.
But It’s Not for Everyone
While anyone can trade, not everyone should. Trading requires discipline, patience, and the ability to handle losses without panic. If you’re only looking for “quick riches” or can’t afford to lose your money, trading might not be the right fit.
The Risk Reality
Trading offers opportunity, but it also comes with significant risk. Many beginners focus on the potential for profit without considering the challenges. Understanding these realities early can help you avoid costly mistakes.
Profits and Losses Go Hand in Hand
Every trade has two possible outcomes: you either win or lose. Even professional traders who have years of experience don’t win 100% of the time. Losses are part of trading, and they cannot be avoided completely. The key is to make sure that when you lose, you lose small, and when you win, you aim to win bigger. This balance is what allows traders to grow their accounts over time.
Quote from William O’Neil “The whole secret to winning and losing in the stock market is to lose the least amount possible when you’re not right.”
The Power of Risk Management
Good traders know that managing risk is just as important as finding opportunities. This includes setting stop-loss orders to limit potential losses, deciding how much of your account to risk on each trade (often no more than 1–2%), and avoiding the temptation to go “all in” on a single position. Without risk management, even one bad trade can wipe out your account.
Quote from Paul Tudor Jones “And then at the end of the day, the most important thing is how good are you at risk control. Ninety-percent of any great trader is going to be the risk control.”
Emotional Challenges
Trading is not just about numbers on a screen, it’s also a psychological battle. Fear, greed, and impatience are common emotions that can lead to poor decisions. Fear can cause you to exit trades too soon, missing out on profits. Greed can tempt you to hold onto losing trades, hoping they will recover. Impatience can make you jump into trades without proper analysis. Successful traders develop discipline and stick to a plan, even when emotions are high.
Market Uncertainty
No one can predict the market with absolute certainty. Economic news, political events, or unexpected global crises can move prices in ways no analysis could foresee. Accepting this uncertainty is crucial, trading is about probabilities, not guarantees.
Scams and False Promises
The trading world is full of misleading offers. From unregulated brokers to “get rich quick” trading systems, scams are common in fact the FCA reported that from January to August 2024 they received 14,504 reports of unauthorized business.
Always be cautious of anyone promising guaranteed returns or secret strategies. Legitimate trading is never risk-free. Choosing a regulated broker and relying on trusted educational resources is essential.
If you want to find out how to spot a regulated broker and not get scammed. You must read our guide on What is a Regulated Broker, to help you understand more about what is actually regulation in brokers and how to assure them.
The Golden Rule
Never risk money you cannot afford to lose. Trading capital should be separate from money meant for rent, bills, or essentials. Treating trading funds as “risk capital” helps keep your decisions rational and protects your financial stability outside the markets.
Next Step: How to Start Trading?
If you’ve made it this far, you already understand the basics of what trading is, how it differs from investing, and the main markets you can explore. The next step is to go deeper into specific areas.
A natural place to start is Forex trading, since it’s the largest and most accessible market for beginners. You might also want to explore more about stock trading or how to safely choose a broker.
The key is to start small and keep learning. Use demo accounts to practice without risk, read guides, build knowledge step by step and set max risk per trade (e.g., ≤1%) and choose conservative leverage until you have a track record. Don’t rush into trading large amounts, consistency and patience matter more than speed.
Wrap-Up: Trading Is for Everyone If You Start Smart
Trading is no longer just for Wall Street professionals. With today’s apps and platforms, anyone with an internet connection can try it. But accessibility doesn’t mean it’s easy success. It requires preparation, discipline, and the ability to manage risk.
If you approach trading with the right mindset, small steps, steady learning, and realistic expectations, you’ll give yourself the best chance to grow and succeed over time.
Continue Your Trading Journey
If you’re curious about other markets, our next guide, "What Is Crypto Trading – A Beginner’s Guide", explains how cryptocurrency trading works, the risks to consider, and how to get started safely.
When you’re ready to open a trading account, be sure to work with a regulated platform and apps. Our Best Trading Platforms of 2025 page compares trusted platforms side by side to help you choose one that fits your trading goals.
Legal disclaimer
This is educational content only. Nothing on this page is financial advice. Trading involves risks. Past performance does not guarantee future results. Always verify broker licensing on official regulator portals.
Beginner FAQ
How much money do I need to start trading?
You don’t need thousands to begin. Many brokers let you open an account with as little as $50–$100. However, starting with a slightly larger amount (like $200–$500) gives you more flexibility to manage trades and learn properly. Always use money you can afford to lose.
Do I need special software?
No complicated setups are required. Most brokers provide free platforms or mobile apps where you can trade directly. Popular platforms like MetaTrader or TradingView offer charts and tools, but even a simple mobile app can be enough to start.
Can I trade with a job or school schedule?
Yes, but it depends on your approach. Short-term trading (day trading) requires constant attention, which can be hard if you’re busy. Long-term trading or “swing trading” allows you to check the markets once or twice a day, making it easier to balance with work or studies.



